Custom peptide synthesis

Severn Biotech has been making bespoke synthetic peptides since 1993.Peptides are synthesised using Fmoc chemistry on a solid phase support matrix. The final quality of the peptide product is assured by Maldi-TOF Mass spectroscopy, *Electro-spray MS and RP-HPLC analysis. Quantities normally supplied are within the range 1mg-30g. There is a wide range of synthetic peptide modifications and conjugations available,which can be incorporated into the product as part of the service. Peptides are supplied lyophilised and can also be aliquoted into vials specific to cilents requirements
Purity Levels and Peptide Purification
The standard purity is > 85% which is sufficient for antigenic peptides for immunological applications. Ultra-pure peptides of > 95% are obtained by semi-preparative and preparative scale C18 reverse phase HPLC; recommended for bio-active and intracellular studies. All peptides are supplied with HPLC profile and Mass Spectrum for verification of purity and molecular weight. Net peptide content by *amino acid analysis can also be supplied. (*Available on request)
Additional Modifications to Peptides
- Acetylation – N-terminal
- Phosphorylation – available at serine, threonine and tyrosine residues
- Biotinylation – N-terminal or C terminal via lysine (both primary amine)
- Cyclisation (disulphide or cyclic formation)
- Fluorescent labelling ( Flourescein, Cy-Dyes, etc)
- Carrier Protein Conjugation ( KLH, BSA etc)
- Farnesylation , Thioester formation etc
- Hexanoic acid,Octanoyl additon etc
- Isotope labelling (Non radioactive)
Many other modifications are available upon request.
Peptide Ordering
For Peptide ordering click here.
Enquiries and Ordering
Please use the 3 letter or single letter Amino Acid code when making enquiries or ordering synthetic peptides. Please indicate the quantity and level of purity required. Should you need any help or advice we will be happy to answer any questions you may have.
Order Enquiry Example
A Peptide Sequence is written from the “N”(amino) terminus to the “C”(carboxyl) terminus.
GKYTVALMDQRRSTGC 16 amino acids Required Quantity 10mg >95% Purity.
Price Quotation Estimate
Please supply the peptide sequence required, should you need a price estimate quotation for the molecule quickly. Please submit this in the notation above and we will contact you immediately to discuss your enquiry. All enquiries are treated with the strictest confidence and no information supplied will be used or forwarded to third parties. Severn Biotech is happy to engage in confidentiality agreements where the client feels the molecular information is their Intellectual Property. For further details please enquire.
Amino Acid Codes used in Peptide Synthesis
| Name> | 3-letter code | 1-letter code |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Histidine | His | H> |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Lysine | Lys | K |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Proline | Pro | P |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y |
| Valine | Val | V |


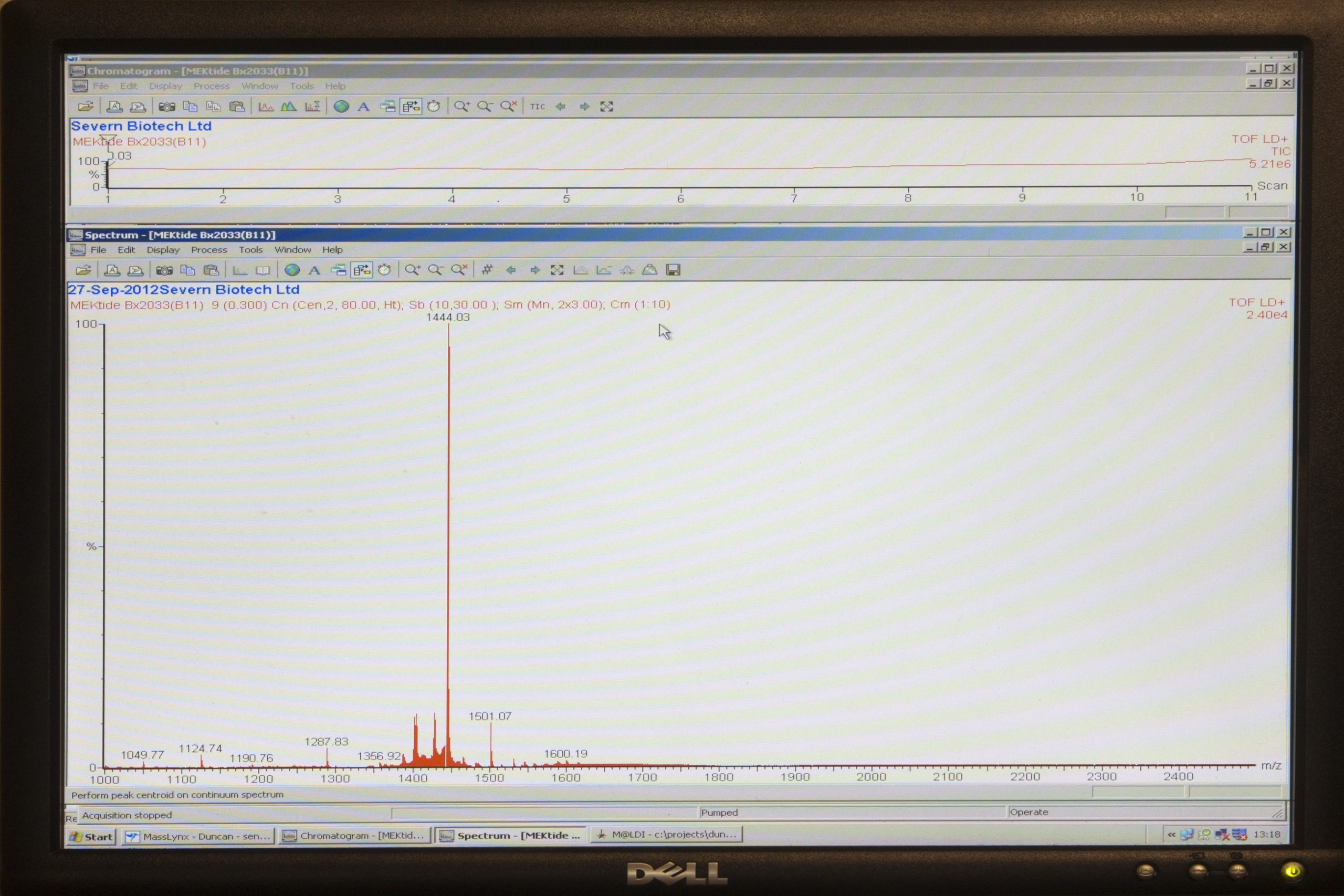
Severn Biotech’s bench top MALDI-TOF Mass Spec used in Verification of peptides
Conjugation to Carrier Proteins (Used as Antigen or Hapten in Anti-sera production)
Synthetic Peptides can be conjugated to various carrier proteins for example BSA, KLH, PPD, Thyroglobulin etc using either a hetero- or homobifunctional cross-linking reagent.Peptides are coupled via a carboxy or amino terminal cysteine residue to available amines on the carrier protein. In order to facilitate this reaction a Cysteine residue must be either part of the peptide or added to the N or C terminus. The product is lyophilised in sterile water or PBS. For further details please enquire.
Multiple Antigenic Peptides (MAPs used in Producing Anti-Peptide Antibodies)
Traditionally, small peptide fragments are attached to a large, inert carrier protein to generate an adequate immune response. The multiple antigenic peptide approach eliminates the need for a carrier protein. This is replaced by a branched chain poly-lysine core of low antigenicity. To this core can be added 2,4,8 or 16 antigenic peptides. The result being a stable structure with a high ratio of peptide to core. The poly-lysine core is sufficient for attachment to plastic, thereby performing well in direct immunoassays.
Handling Synthetic Peptides
Supply and Storage of Peptides
Custom-made synthetic peptides are supplied lyophilised to avoid degradation of the product. The majority of peptides, if stored tightly sealed and at -20°C in lyophilised form will remain stable for several years. To maintain stability, it is recommended that vials should be allowed to warm to room temperature in a dessicator with fresh dessicant before opening to prevent condensation forming on the product.
Peptides in solution are much less stable. Storage is recommended at -20°C in a buffered solution at pH 5-7. To avoid bacterial degradation, sterile purified water must be used for dissolution or the solution should be filtered using a 0.45m or 02m filter. The peptide stock solution should be aliquoted out before freezing to prevent damage caused by repeated freezing and thawing. After thawing, any remaining peptide in an aliquot should be discarded.
Dissolving Peptides
The secondary structure of peptides is often a hindrance to its dissolution, particularly with hydrophobic peptides. Since the formation of this secondary structure may be promoted by salts, the peptide should first be dissolved in sterile distilled or deionised water. At this stage the concentration of the peptide should be kept higher than the required final concentration to allow for addition of other solubilising agents (if required) and buffer salts which should be added only after the peptide is fully dissolved. Peptides containing cysteine, tryptophan or methionine are particularly susceptible to oxidation and should therefore be dissolved in oxygen-free water (prepared by degassing under reduced pressure or by sparging with an inert gas).
If the peptide does not dissolve in pure water, the following measures may be taken:
Sonication. This may help to break up any particles and increase the rate of dissolution.
Dilute aqueous acetic acid or ammonia(10%v/v) added dropwise to basic or acidic peptides respectively.
If the above methods do not succeed in dissolving the peptide, addition of a chaotropic agent such DMF, Urea or Guanidium hydrochloride may be helpful. Addition should be dropwise until the peptide dissolves. These agents may interfere with biological systems so should only be used if the peptide is being prepared for analytical purposes.Salts may need to be removed by dialysis prior to use in biological systems.
